3. RenJS
RenJS allows developers to hook in to RenVM's growing network of bridged chains and assets. It's the official JavaScript SDK for interacting with RenVM and for bridging assets.
Installing and Initializing RenJS
There are two packages that need to be installed:
@renproject/renimplements the core logic for interacting with RenVM@renproject/chainsprovides support for various assets and chains. These can also be imported separately - e.g. using@renproject/chains-ethereumfor Ethereum.
- npm
- yarn
npm install --save @renproject/ren@v2 @renproject/chains@v2
yarn add @renproject/ren@v2 @renproject/chains@v2
Import the packages at the top of App.js:
import RenJS from "@renproject/ren";
import { Bitcoin, Ethereum } from "@renproject/chains";
Initialize RenJS, adding it to your App.js state (line 17) like so:
this.state = {
balance: 0,
message: "",
renJS: new RenJS("testnet", { useV2TransactionFormat: true }),
error: "",
};
We initialize it with the parameter "testnet" to connect to RenVM's testnet. Omit this parameter when you are ready to integrate on mainnet.
Bridging BTC onto Ethereum
There's two steps involves in creating new renBTC tokens on Ethereum - 1) locking BTC and 2) minting renBTC. The method on RenJS to initiate this process is lockAndMint.
Here's what it looks like to set-up a lockAndMint to a user's address on Ethereum:
const { web3, renJS } = this.state;
const mint = await renJS.lockAndMint({
asset: "BTC",
from: Bitcoin(),
to: Ethereum(web3.currentProvider).Address("0x1234..."),
});
For our example, we want to send BTC to a smart contract, not just a user's address. To do this, we specify the details needed to call the smart contract. Add this to the body of deposit:
const { web3, renJS } = this.state;
this.log(`Generating deposit address...`);
const amount = 0.003; // BTC
const mint = await renJS.lockAndMint({
// Send BTC from the Bitcoin blockchain to the Ethereum blockchain.
asset: "BTC",
from: Bitcoin(),
to: Ethereum(web3.currentProvider).Contract({
// The contract we want to interact with
sendTo: contractAddress,
// The name of the function we want to call
contractFn: "deposit",
// Arguments expected for calling `deposit`
contractParams: [
{
name: "_msg",
type: "bytes",
value: Buffer.from(`Depositing ${amount} BTC`),
},
],
}),
});
Each LockAndMint object has a unique gateway address, generated from the details we provided to it. We want to show the gateway address to the user and then wait for them to send BTC to this address. Add the following log:
// Show the gateway address to the user so that they can transfer their BTC to it.
this.log(`Deposit ${amount} BTC to ${mint.gatewayAddress}`);
To handle deposits received at the gateway address, the mint object emits "deposit" events that can be listened to using mint.on("deposit", ...). After detecting a deposit, there's three steps for completing the asset bridging:
- waiting for the deposit to be confirmed,
- submitting the deposit to RenVM and wait for a signature, and
- submitting to the mint-chain - in our example this is Ethereum.
We perform these steps inside the "deposit" event callback:
mint.on("deposit", async (deposit) => {
// Details of the deposit are available from `deposit.depositDetails`.
const hash = deposit.txHash();
const depositLog = (msg) =>
this.log(
`BTC deposit: ${Bitcoin.utils.transactionExplorerLink(
deposit.depositDetails.transaction,
"testnet"
)}\n
RenVM Hash: ${hash}\n
Status: ${deposit.status}\n
${msg}`
);
await deposit
.confirmed()
.on("target", (target) => depositLog(`0/${target} confirmations`))
.on("confirmation", (confs, target) =>
depositLog(`${confs}/${target} confirmations`)
);
await deposit
.signed()
// Print RenVM status - "pending", "confirming" or "done".
.on("status", (status) => depositLog(`Status: ${status}`));
await deposit
.mint()
// Print Ethereum transaction hash.
.on("transactionHash", (txHash) =>
this.log(`Ethereum transaction: ${String(txHash)}\nSubmitting...`)
);
this.log(`Deposited ${amount} BTC.`);
});
deposit.status returns the current progress of the deposit, and will be one of "detected", "confirmed", "signed", "submitted" or "reverted". (See DepositStatus docs)
In addition to receiving .on("deposit", ...) events, you can also manually provide the details of a deposit using mint.processDeposit. The parameter should match the type of deposit.depositDetails of a deposit object returned from.on("deposit", ...).
Bridging BTC back from Ethereum
In order to return the BTC back from Ethereum, the renBTC must be burned, and a recipient BTC address nominated. RenVM will automatically see and process the burn, releasing the BTC to the recipient. RenJS can be used to:
- initiate a burn by providing it the details to burn the renBTC, or
- monitor an existing burn by providing it with the transaction hash or identifier of the burn.
Initiating a burn looks like the following:
const { web3, renJS, balance } = this.state;
const recipient = prompt("Enter BTC recipient:");
const amount = balance;
const burnAndRelease = await renJS.burnAndRelease({
// Send BTC from Ethereum back to the Bitcoin blockchain.
asset: "BTC",
to: Bitcoin().Address(recipient),
from: Ethereum(web3.currentProvider).Contract((btcAddress) => ({
sendTo: contractAddress,
contractFn: "withdraw",
contractParams: [
{
type: "bytes",
name: "_msg",
value: Buffer.from(`Withdrawing ${amount} BTC`),
},
{
type: "bytes",
name: "_to",
value: btcAddress,
},
{
type: "uint256",
name: "_amount",
value: RenJS.utils.toSmallestUnit(amount, 8),
},
],
})),
});
let confirmations = 0;
await burnAndRelease
.burn()
// Ethereum transaction confirmations.
.on("confirmation", (confs) => {
confirmations = confs;
})
// Print Ethereum transaction hash.
.on("transactionHash", (txHash) => this.log(`txHash: ${String(txHash)}`));
await burnAndRelease
.release()
// Print RenVM status - "pending", "confirming" or "done".
.on("status", (status) =>
status === "confirming"
? this.log(`${status} (${confirmations}/15)`)
: this.log(status)
)
// Print RenVM transaction hash
.on("txHash", this.log);
this.log(`Withdrew ${amount} BTC to ${recipient}.`);
Complete App.js
Your App.js file should now look like this (don't forget to replace the contract address):
import React from "react";
import RenJS from "@renproject/ren";
import { Bitcoin, Ethereum } from "@renproject/chains";
import Web3 from "web3";
import "./App.css";
import ABI from "./ABI.json";
// Replace with your contract's address.
const contractAddress = "0x3Aa969d343BD6AE66c4027Bb61A382DC96e88150";
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
balance: 0,
message: "",
error: "",
renJS: new RenJS("testnet", { useV2TransactionFormat: true }),
};
}
componentDidMount = async () => {
let web3Provider;
// Initialize web3 (https://medium.com/coinmonks/web3-js-ethereum-javascript-api-72f7b22e2f0a)
// Modern dApp browsers...
if (window.ethereum) {
web3Provider = window.ethereum;
try {
// Request account access
await window.ethereum.enable();
} catch (error) {
// User denied account access...
this.logError("Please allow access to your Web3 wallet.");
return;
}
}
// Legacy dApp browsers...
else if (window.web3) {
web3Provider = window.web3.currentProvider;
}
// If no injected web3 instance is detected, fall back to Ganache
else {
this.logError("Please install MetaMask!");
return;
}
const web3 = new Web3(web3Provider);
const networkID = await web3.eth.net.getId();
if (networkID !== 42) {
this.logError("Please set your network to Kovan.");
return;
}
this.setState({ web3 }, () => {
// Update balances immediately and every 10 seconds
this.updateBalance();
setInterval(() => {
this.updateBalance();
}, 10 * 1000);
});
};
render = () => {
const { balance, message, error } = this.state;
return (
<div className="App">
<p>Balance: {balance} BTC</p>
<p>
<button onClick={() => this.deposit().catch(this.logError)}>
Deposit 0.003 BTC
</button>
</p>
<p>
<button
onClick={() => this.withdraw().catch(this.logError)}
>
Withdraw {balance} BTC
</button>
</p>
{message.split("\n").map((line) => (
<p>{line}</p>
))}
{error ? <p style={{ color: "red" }}>{error}</p> : null}
</div>
);
};
updateBalance = async () => {
const { web3 } = this.state;
const contract = new web3.eth.Contract(ABI, contractAddress);
const balance = await contract.methods.balance().call();
this.setState({ balance: parseInt(balance.toString()) / 10 ** 8 });
};
logError = (error) => {
console.error(error);
this.setState({ error: String((error || {}).message || error) });
};
log = (message) => {
this.setState({ message });
};
deposit = async () => {
this.logError(""); // Reset error
const { web3, renJS } = this.state;
this.log(`Generating deposit address...`);
const amount = 0.003; // BTC
const mint = await renJS.lockAndMint({
// Send BTC from the Bitcoin blockchain to the Ethereum blockchain.
asset: "BTC",
from: Bitcoin(),
to: Ethereum(web3.currentProvider).Contract({
// The contract we want to interact with
sendTo: contractAddress,
// The name of the function we want to call
contractFn: "deposit",
// Arguments expected for calling `deposit`
contractParams: [
{
name: "_msg",
type: "bytes",
value: Buffer.from(`Depositing ${amount} BTC`),
},
],
}),
});
// Show the gateway address to the user so that they can transfer their BTC to it.
this.log(`Deposit ${amount} BTC to ${mint.gatewayAddress}`);
mint.on("deposit", async (deposit) => {
// Details of the deposit are available from `deposit.depositDetails`.
const hash = deposit.txHash();
const depositLog = (msg) =>
this.log(
`BTC deposit: ${Bitcoin.utils.transactionExplorerLink(
deposit.depositDetails.transaction,
"testnet"
)}\n
RenVM Hash: ${hash}\n
Status: ${deposit.status}\n
${msg}`
);
await deposit
.confirmed()
.on("target", (target) =>
depositLog(`0/${target} confirmations`)
)
.on("confirmation", (confs, target) =>
depositLog(`${confs}/${target} confirmations`)
);
await deposit
.signed()
// Print RenVM status - "pending", "confirming" or "done".
.on("status", (status) => depositLog(`Status: ${status}`));
await deposit
.mint()
// Print Ethereum transaction hash.
.on("transactionHash", (txHash) =>
depositLog(`Mint tx: ${txHash}`)
);
this.log(`Deposited ${amount} BTC.`);
});
};
withdraw = async () => {
this.logError(""); // Reset error
const { web3, renJS, balance } = this.state;
const recipient = prompt("Enter BTC recipient:");
const amount = balance;
const burnAndRelease = await renJS.burnAndRelease({
// Send BTC from Ethereum back to the Bitcoin blockchain.
asset: "BTC",
to: Bitcoin().Address(recipient),
from: Ethereum(web3.currentProvider).Contract((btcAddress) => ({
sendTo: contractAddress,
contractFn: "withdraw",
contractParams: [
{
type: "bytes",
name: "_msg",
value: Buffer.from(`Withdrawing ${amount} BTC`),
},
{
type: "bytes",
name: "_to",
value: btcAddress,
},
{
type: "uint256",
name: "_amount",
value: RenJS.utils.toSmallestUnit(amount, 8),
},
],
})),
});
let confirmations = 0;
await burnAndRelease
.burn()
// Ethereum transaction confirmations.
.on("confirmation", (confs) => {
confirmations = confs;
})
// Print Ethereum transaction hash.
.on("transactionHash", (txHash) =>
this.log(
`Ethereum transaction: ${String(txHash)}\nSubmitting...`
)
);
await burnAndRelease
.release()
// Print RenVM status - "pending", "confirming" or "done".
.on("status", (status) =>
status === "confirming"
? this.log(`${status} (${confirmations}/15)`)
: this.log(status)
)
// Print RenVM transaction hash
.on("txHash", (hash) => this.log(`RenVM hash: ${hash}`));
this.log(`Withdrew ${amount} BTC to ${recipient}.`);
};
}
export default App;
Testing it
If you click "Deposit 0.003 BTC", it should show you a Bitcoin address:
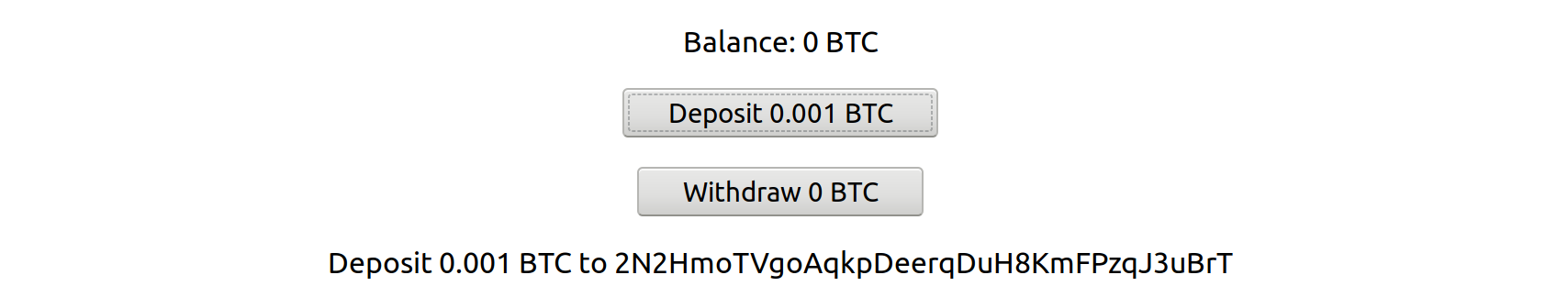
If you don't already have Testnet BTC, you'll need to go to a Bitcoin Testnet faucet (we recommend https://testnet-faucet.mempool.co).
Send 0.003 BTC to the Bitcoin gateway address to continue. RenJS will wait for two confirmations before continuing, which may take around 15-20 minutes.
After completing all the steps, you should see the balance increase by 0.003 BTC, minus fees (currently a 0.001 BTC transfer fee and 0.25% RenVM fee).
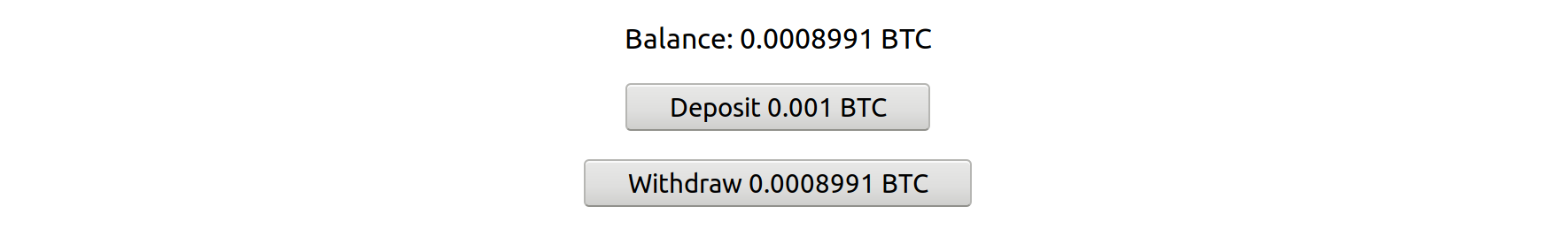
Test withdrawing as well. If you don't have a Testnet BTC address to give it, the faucet lists a return address you can use. You should see the balance go back to 0 and the Bitcoin address you entered receive the BTC (again, some transfer fees will be deducted).
tip
You can find the site deployed here as well: https://renproject.github.io/renjs-tutorial
tip
You can visit the Blog to find more tutorials or examples.
caution
The above tutorial includes basic usage of RenJS. If you are building a production site, continue to the next sections, including Resuming transfers and RenVM UX Best Practice.